|
I am a PhD graduate from the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC); currently a Senior Machine Learning Engineer at Bloomberg. I worked under Prof. Cornelia Caragea during my PhD. Email / CV / GitHub / Google Scholar / LinkedIn Contents: (Last updated: 9/13/2024) |

|
Summary of my research and project experiences:
- Recursive Neural Networks: I extended Recursive Neural Networks (RvNN) for length generalization, compositional generalization, and efficiency.
- Recursive Transformers: I explored the incorporation of recursion and dynamic halting in Transformers.
- Language Models: I explored LLMs for decomposed reasoning with chain-of-thoughts/tree-of-thoughts-like prompting strategies and self-evaluation. I customized GPT2 for novelty-controlled paraphrase generation with parameter-efficient fine-tuning. I created a conversational AI equipped with DialoGPT and FAISS-based vector search.
- Location Attention: I have worked on novel forms of location attention for length generalization using Seq2Seq models.
- Keyphrase Generation: I have extensive experience on keyphrase generation involving Seq2Seq models (including pre-trained models like T5/BART).
- Social Media Information Extraction: I have experience in social-media (Twitter-related) dataset creation and pre-processing for disaster-related information extraction (via NER, Keyphrase Extraction, Multilingual Classification etc.).
- Miscellaneous: I have some experience in a variety of other topics such as - Structured State Space models, Long Convolution, Transformer variants, curriculum learning, meta-learning, contrastive learning, question generation, question answering, summarization, data augmentation, grounded language learning, image classification, etc.
|
|
| Recurrent/Recursive Neural Networks |
|
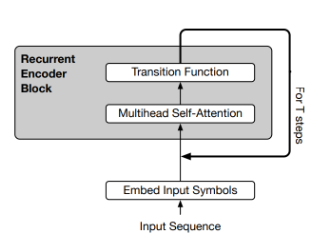
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea ArXiv, 2024 pdf/ code We empirically study the inductive biases of two major approaches to augmenting Transformers with a recurrent mechanism - (1) the approach of incorporating a depth-wise recurrence similar to Universal Transformers; and (2) the approach of incorporating a chunk-wise temporal recurrence like Temporal Latent Bottleneck. |

|
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea ArXiv, 2024 In this paper, we study two classes of models, Recursive Neural Networks (RvNNs) and Transformers, and show that a tight connection between them emerges from the recent development of two recent models - Continuous Recursive Neural Networks (CRvNN) and Neural Data Routers (NDR). The former representing RvNNs. and the latter Transformers. |
|
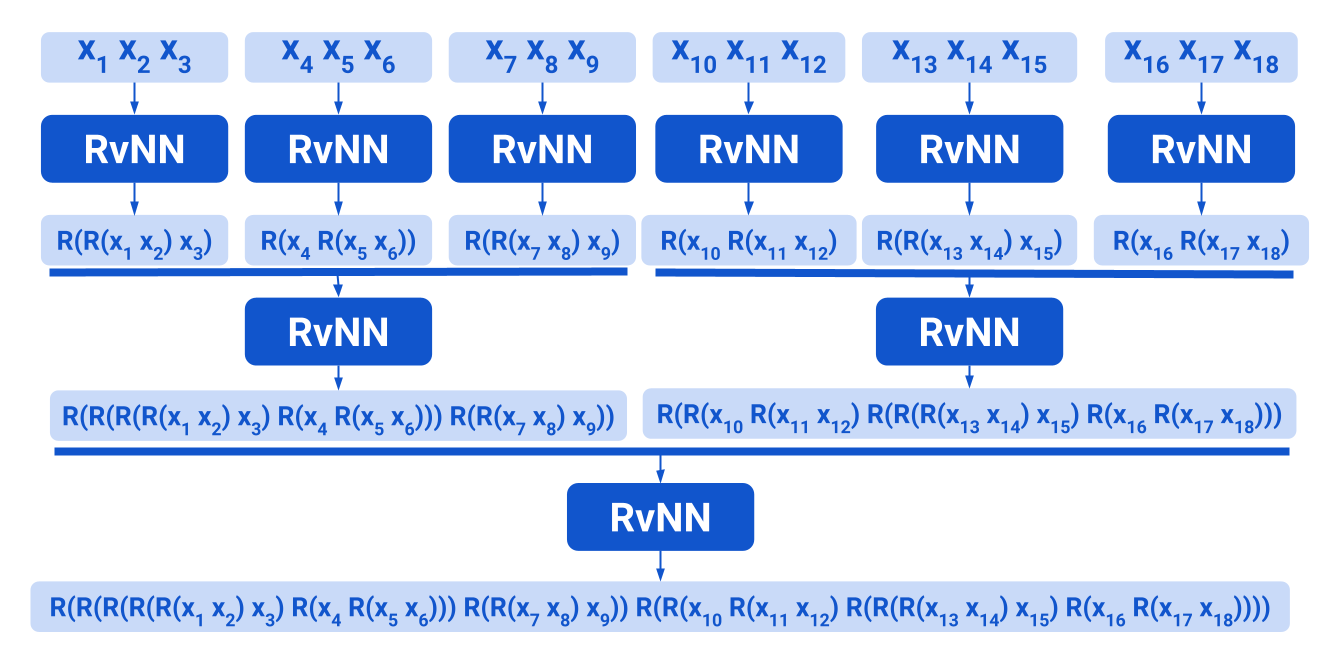
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea NeurIPS, 2023 pdf/ code We implement a Balanced Tree Recursion at a chunk level. Each chunk at any iteration is processed by Efficient Beam Tree Recursive Neural Networks (EBT-RvNN). Thus, Recursion within a Recursion is implemented. This hybrid setup is much more computationally efficient than EBT-RvNN. On the other hand, it still performs competitively in ListOps length generalization and logical inference, unlike fully Balanced Tree models or other models like Transformers/SSMs. The model setup also performs well in the text-related tasks of LRA. |
|
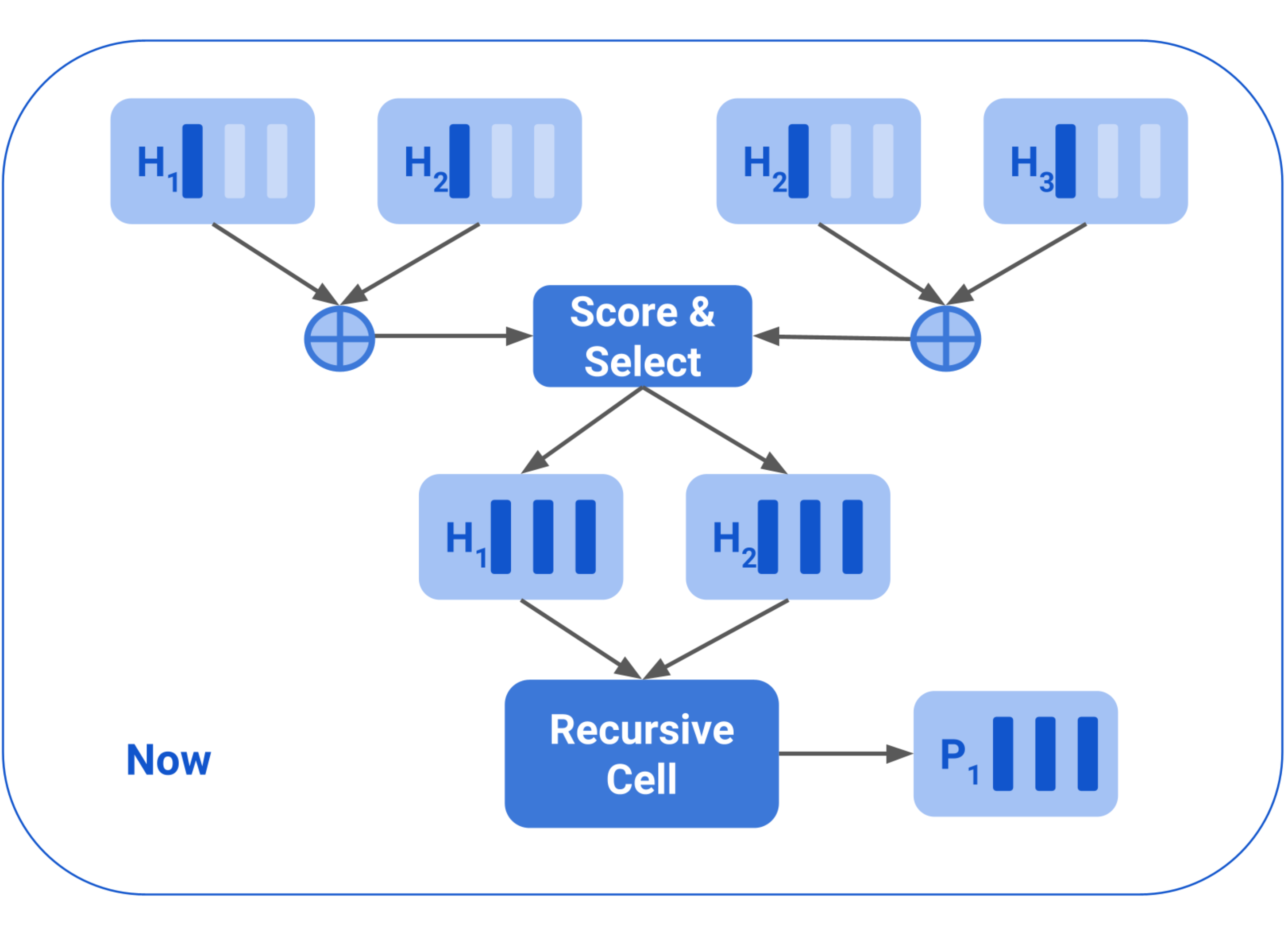
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea NeurIPS, 2023 pdf/ code Beam Tree Recursive Neural Network (BT-RvNN) was recently proposed as a simple extension of Gumbel Tree RvNN. We identify a memory bottleneck in it and remove it leading to 10-16 times less memory consumption. In addition, we also propose a strategy to utilize the induced latent-tree node representations produced by BT-RvNN to turn BT-RvNN from a sentence encoder into a sequence contextualizer by sending top-down signals from the parent node to leaf nodes using attention. This opens up a way to interface BT-RvNN with other downstream modules like Transformers. |
|
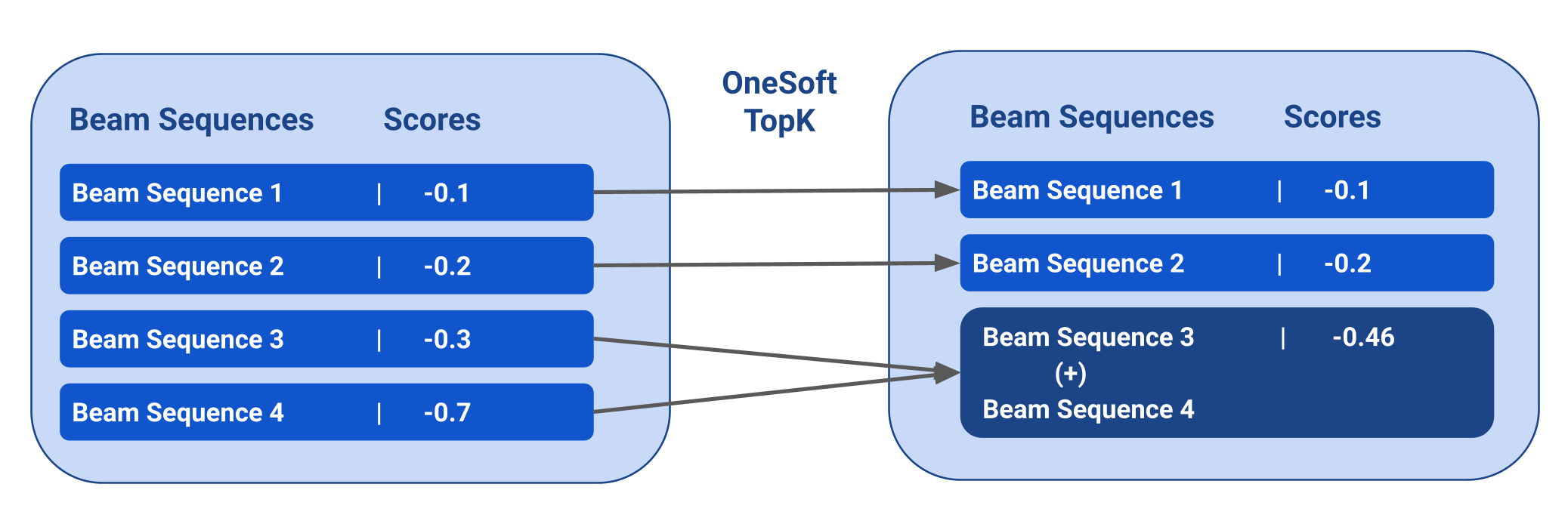
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea ICML, 2023 pdf / code We extend Gumbel Tree LSTM by replacing Gumbel softmax with a soft top-k mechanism and use it for beam search instead of greedy easy-first parsing. This simple method performs competitively with other more sophisticated implementations of RvNNs. Our proposed soft top-k mechanism can be explored further for other tasks where sending gradient signals through some top-k is deemed important. |
|
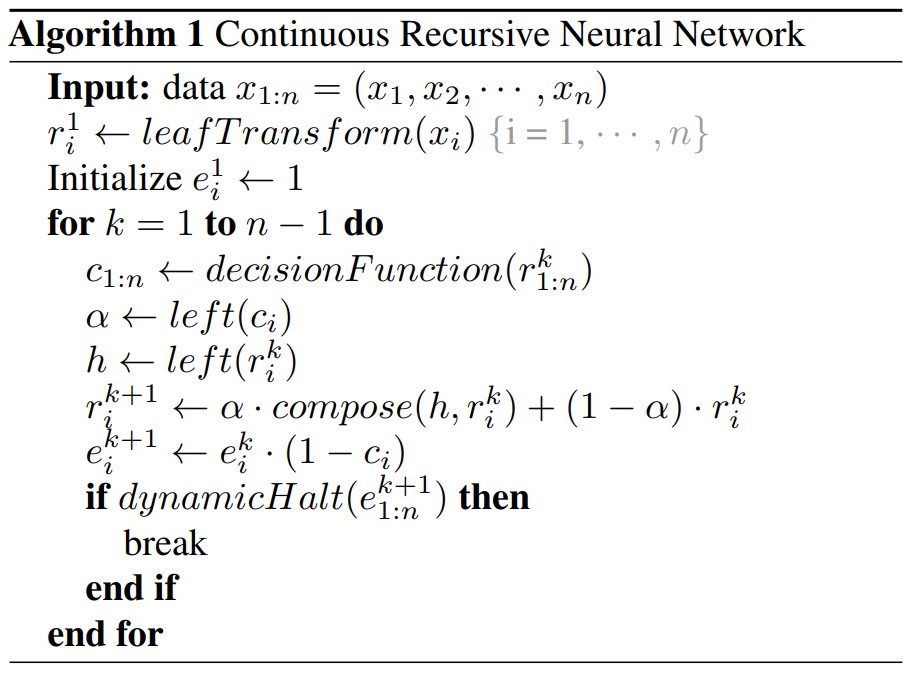
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea ICML (Long Talk), 2021 pdf / code / Talk We propose Continuous Recursive Neural Network (CRvNN) as a backpropagation-friendly implementation of RvNNs without surrogate gradients, reinforcement learning, or stack-augmented recurrent operations. This is done by incorporating a continuous relaxation to the induced structure. |
| OOD-Generalization, Length Generalization |
|
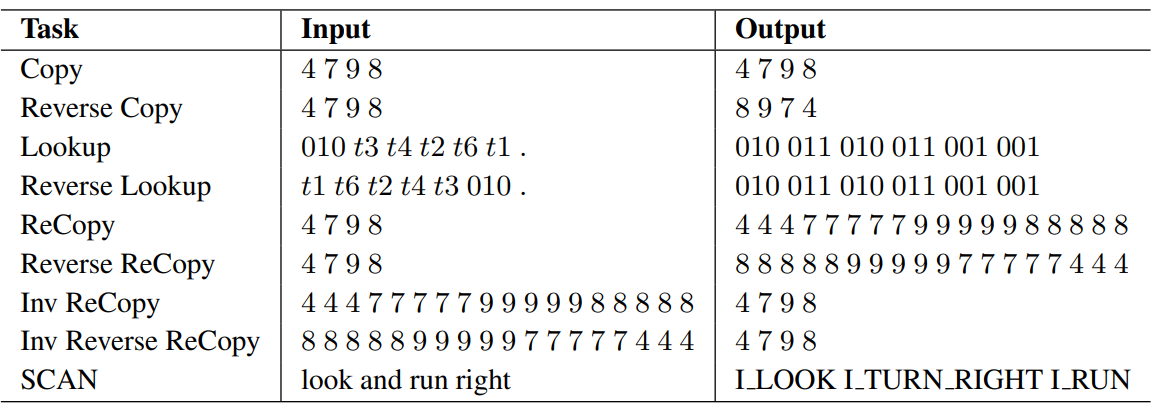
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea ICML, 2023 pdf / code We explore different ways to utilize position-based cross-attention in seq2seq networks to enable length generalization in algorithmic tasks. |
| Prompt Tuning/Engineering |
|
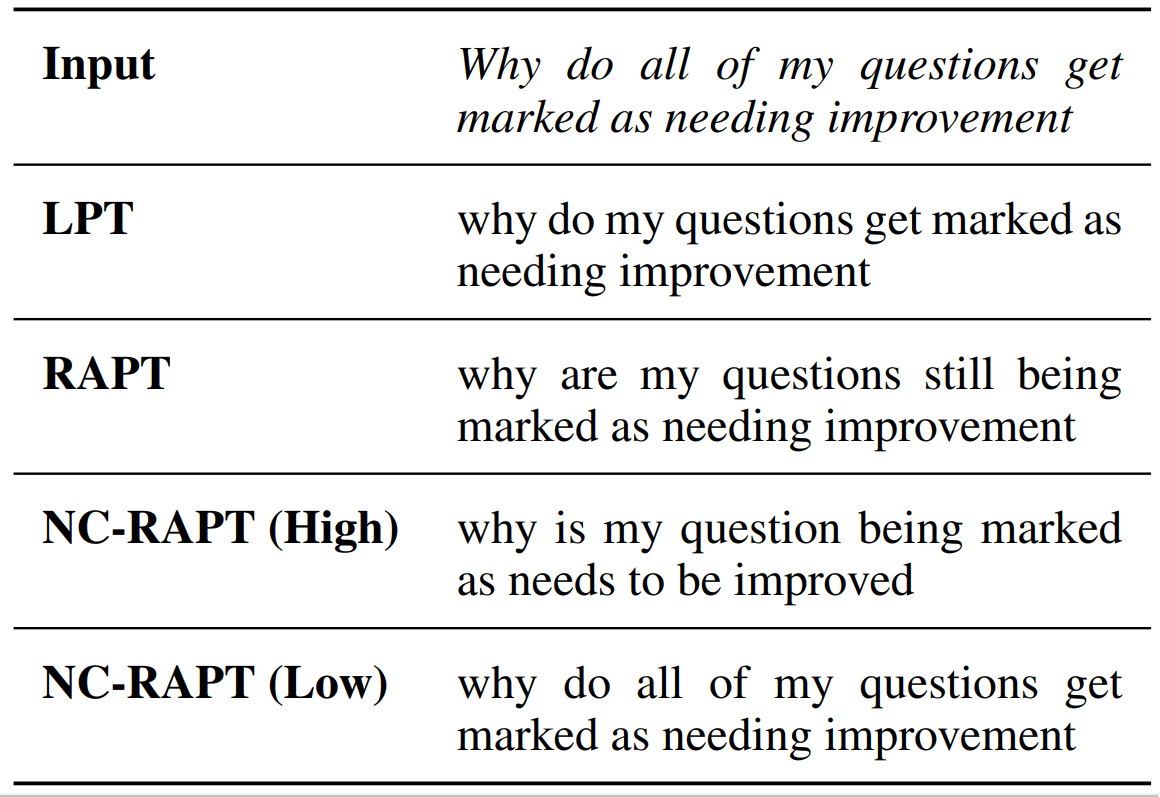
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Yong Zhuang, Shuyi Wang AAAI (Oral), 2022 We concentrate on two contributions to paraphrase generation: (1) we propose Retrieval Augmented Prompt Tuning (RAPT) as a parameter-efficient method to adapt large pre-trained language models for paraphrase generation; (2) we propose Novelty Conditioned RAPT (NC-RAPT) as a simple model-agnostic method of using specialized prompt tokens for controlled paraphrase generation with varying levels of lexical novelty. |
| Keyphrase Generation |
|
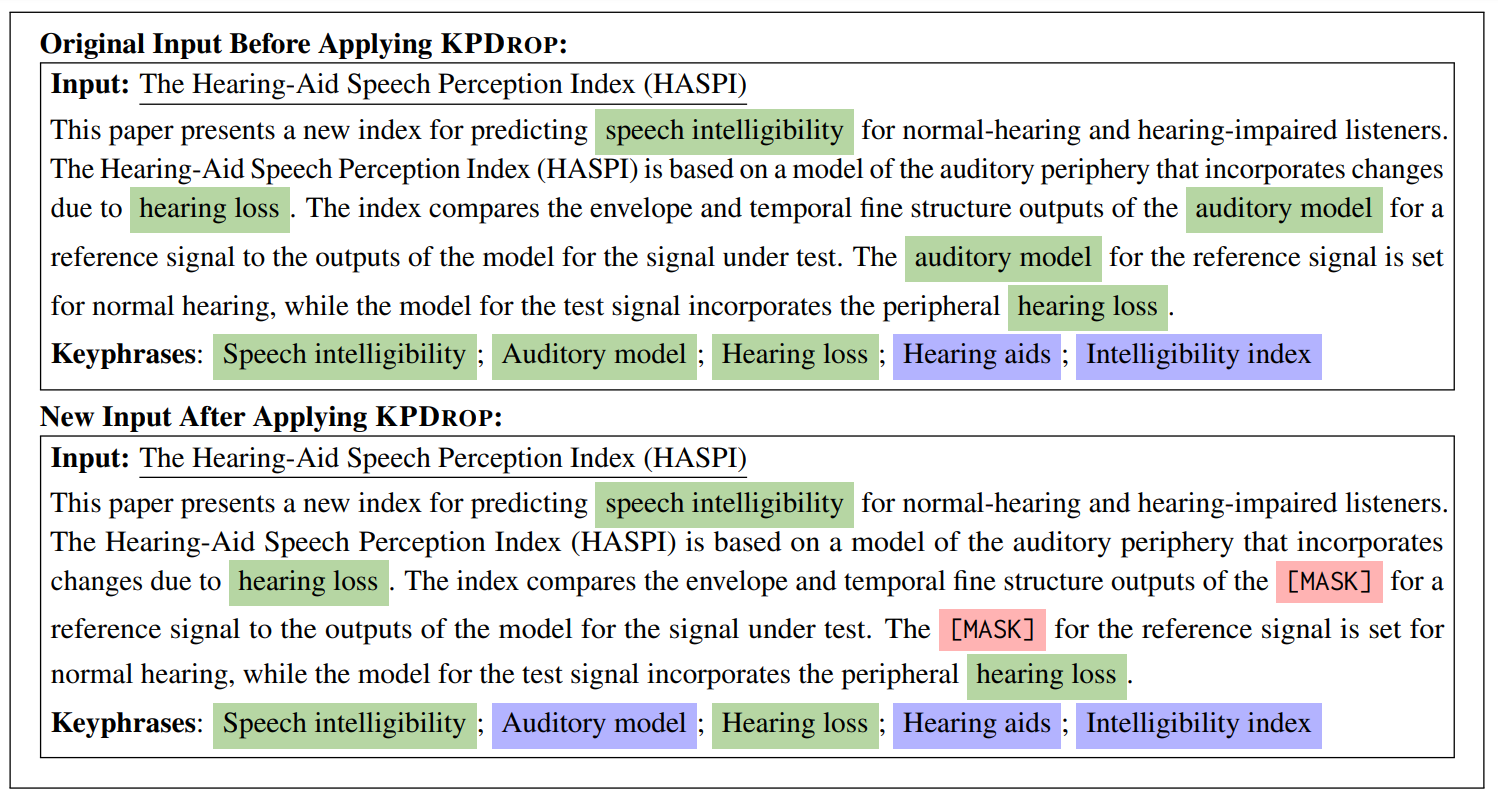
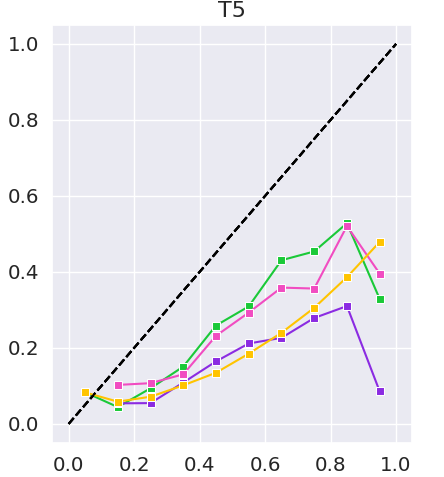
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Seo Yeon Park *, Tuhin Kundu *, Cornelia Caragea EMNLP Findings, 2023 pdf / code We propose a model-agnostic approach called keyphrase dropout (or KPDrop) to improve absent keyphrase generation. In this approach, we all instances of some randomly chosen present keyphrases from the document and turn them into artificial absent keyphrases during training. We also explore the benefits of this method in a semi-supervised training regime. |
|
Tuhin Kundu, Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea ArXiv 2023 we study various tendencies exhibited by three strong models: T5 (based on a pre-trained transformer), CatSeq-Transformer (a non-pretrained Transformer), and ExHiRD (based on a recurrent neural network). We analyze prediction confidence scores, model calibration, and the effect of token position on keyphrases generation. Moreover, we motivate and propose a novel metric framework, SoftKeyScore, to evaluate the similarity between two sets of keyphrases by using softscores to account for partial matching and semantic similarity |
|
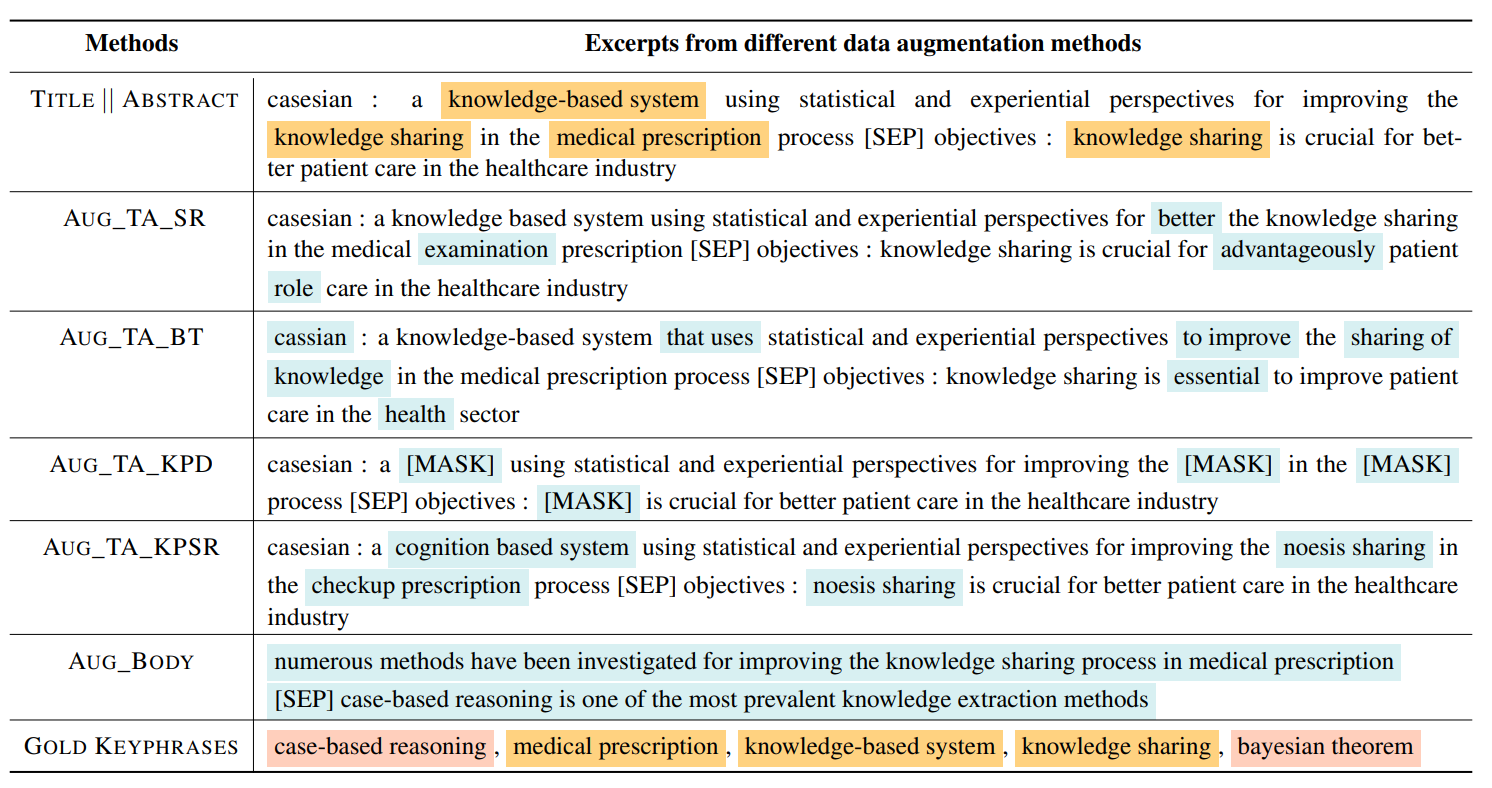
Krishna Garg Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea ACL Findings, 2023 pdf / code We present data augmentation strategies specifically to address keyphrase generation in purely resource-constrained domains. We design techniques that use the full text of the articles to improve both present and absent keyphrase generation |
|
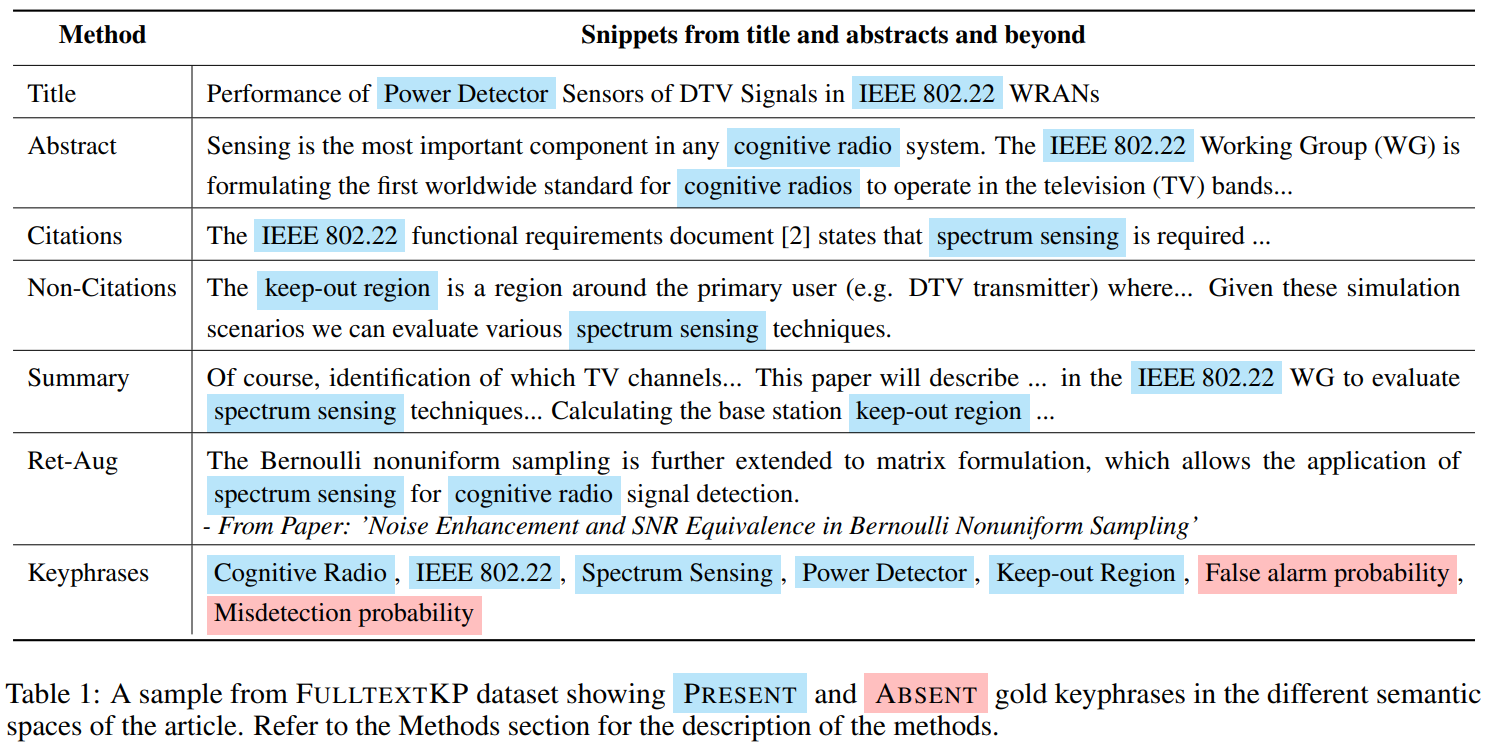
Krishna Garg Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea EMNLP Findings, 2022 pdf / code We comprehensively explore whether the integration of additional information from the full text of a given article or from semantically similar articles can be helpful for a neural keyphrase generation model or not. We discover that adding sentences from the full text, particularly in the form of the extractive summary of the article can significantly improve the generation of both types of keyphrases that are either present or absent from the text. |
| Question Generation |
|
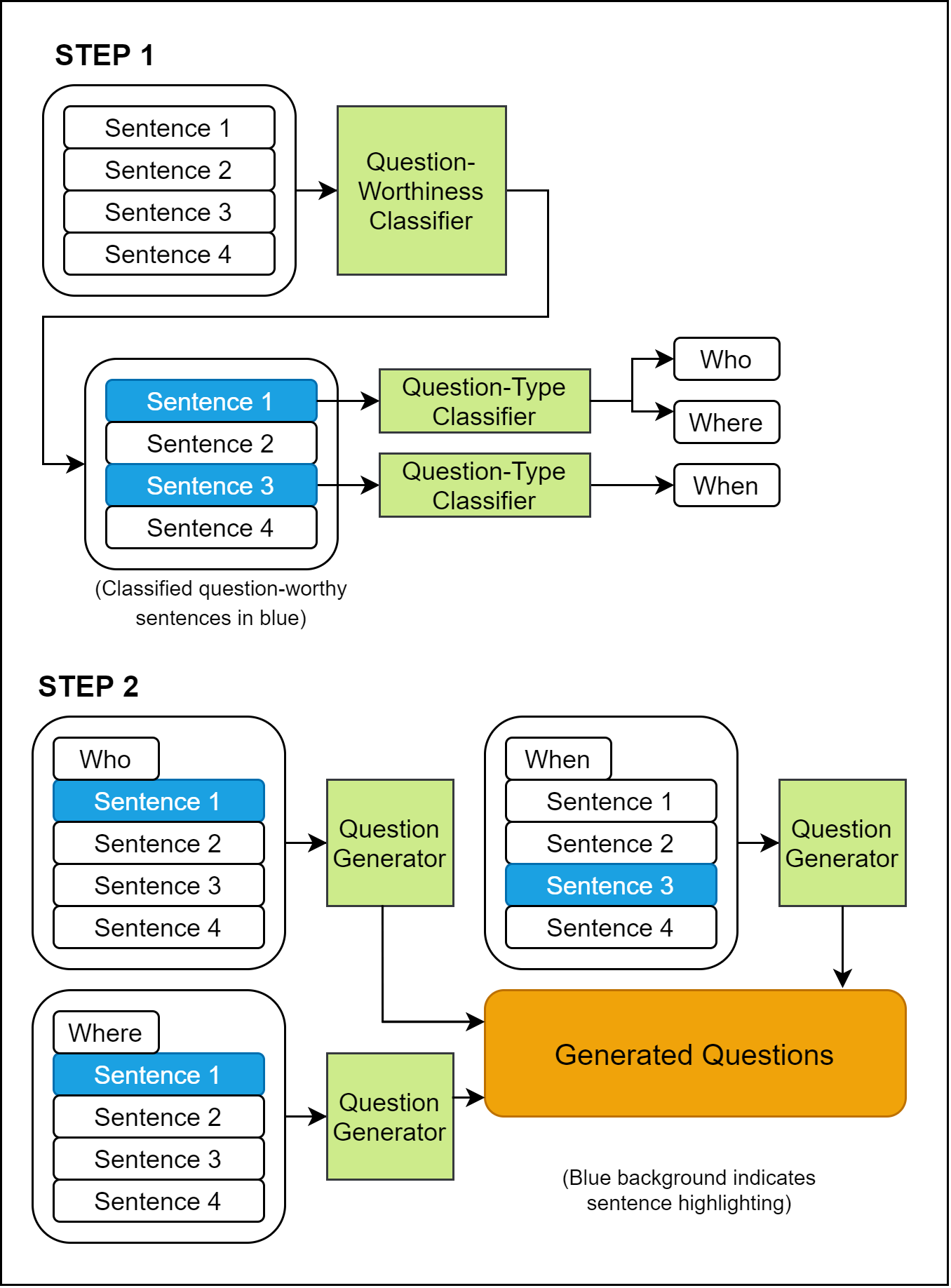
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea, Debanjan Mahata ArXiv 2022 pdf / code We study the task of predicting a set of salient questions from a given paragraph without any prior knowledge of the precise answer. We make two main contributions. First, we propose a new method to evaluate a set of predicted questions against the set of references by using the Hungarian algorithm to assign predicted questions to references before scoring the assigned pairs. We show that our proposed evaluation strategy has better theoretical and practical properties compared to prior methods because it can properly account for the coverage of references. Second, we compare different strategies to utilize a pre-trained seq2seq model to generate and select a set of questions related to a given paragraph. |
| Disaster-Related Information Extraction |
|
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea, Doina Caragea ACL SRW, 2020 pdf / code We present a masking-based loss function for partially labeled samples and demonstrate the effectiveness of Manifold Mixup in the text domain. Our main model is based on Multilingual BERT, which we further improve with Manifold Mixup. We show that our model generalizes to unseen disasters in the test set. Furthermore, we analyze the capability of our model for zero-shot generalization to new languages. |
|
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea, Doina Caragea AAAI (Special Track, AI for Social Impact), 2020 pdf / code To facilitate progress on automatic identification (or extraction) of disaster hashtags for Twitter data, we construct a unique dataset of disaster-related tweets annotated with hashtags useful for filtering actionable information. Using this dataset, we further investigate Long Short-Term Memory-based models within a Multi-Task Learning framework. |

|
Jishnu Ray Chowdhury, Cornelia Caragea, Doina Caragea WWW, 2019 We explore keyphrase extraction models for extracting disaster-related keyphrases from tweets. We employ a joint-training-based approach (for keyword discovery and keyphrase extraction). We extend it using contextual word embeddings, POS-tags, phonetics, and phonological features. We also propose an embedding-based metrics to better capture the correctness of the predicted keyphrases. |
|
|

|
code Implementation of an LLM prompting pipeline combined with wrappers for auto-decomposing reasoning steps and for search through the reasoning step space (eg. by beam search, MCTS etc.) guided by self-evaluation rewards. |
|
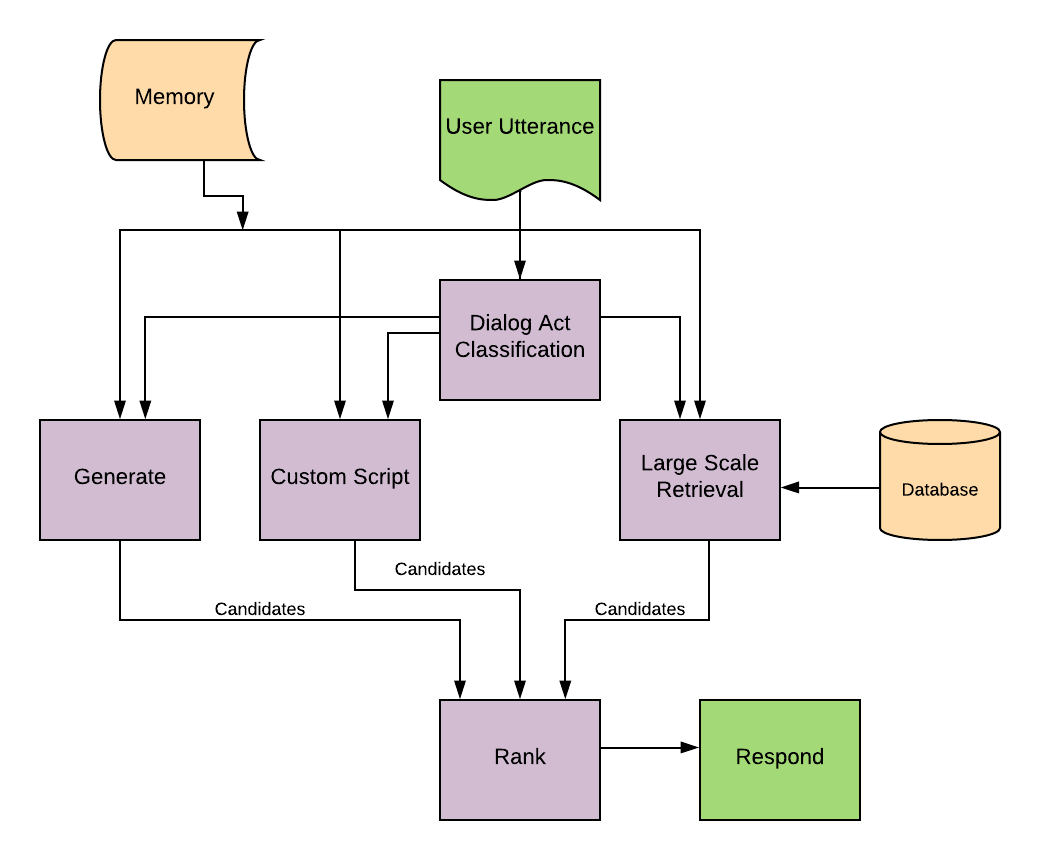
pdf / code / video This is a pre-ChatGPT era model. It uses DialoGPT combined with a response retrieval mechanism from a custom script (can be used for customing personality) and Reddit database. The overall model is a synergy of multiple sub-modules for retrieval, dialog classification, generation, and ranking. It also incorporates a Text-to-Speech Synthesis Mechanism. |
|
code The library allows synergy of different optimization strategies like hypergradient optimization, nostalgia, variance rectification, lookahead, decaying momentum, iterate averaging, gradient checkpointing, gradient noise, quasi-hyperbolic momentum, decorrelated weight decay, and more. |
|
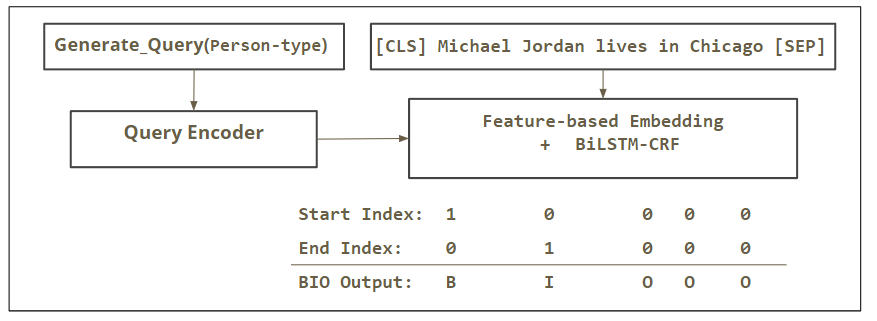
pdf / code We address the challenges posed by noise and emerging/rare entities in Named Entity Recognition task for social media domain. Following the recent advances, we employ Contextualized Word Embeddings from Language Models pre-trained on large corpora along with some normalization techniques to reduce noise. Our best model achieves state-of-the-art (at the time of the project) results (F1 52.47%) on WNUT 2017 dataset. Additionally, we adopt a modular approach to systematically evaluate different contextual embeddings and downstream labeling mechanisms using Sequence Labeling and a Question Answering framework. |
|
pdf / code In this work, I study and compare multiple capsule routing algorithms for text classification, including dynamic routing, Heinsen routing, and capsule-routing-inspired attention-based sentence encoding techniques like dynamic self-attention. We analyze the theoretical connection between attention and capsule routing and contrast the two ways of normalizing the routing weights. Finally, I present a new way to do capsule routing, or rather an iterative refinement, using a richer attention function to measure agreement among output and input capsules and with highway connections in between iterations. |
|
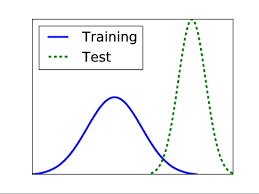
pdf / code Despite the strong predictive performance of Machine Learning models, they are still subject to spurious correlations. Working under the I.I.D. assumption, they are often hard to generalize to out-of-distribution test data. In this project, we tackle the problem of co-variate shift, where the test data is from a different distribution than the training data. Particularly, we approach this problem from a causal framework. We compare IRMv1, CoRe, ICP, and Entropy Penalty (EP) on different settings. Furthermore, we experiment with disentangled representations, and we try to enhance classification results by gating the features of intermediate hidden state representations based on their influence on the classification probabilities. |
|
code Experiments with continuous sparsification of neural network connections and sparse representation (using K-winner activation function) on NLP tasks like Named Entity Recognition. Continuous sparsification could halve the number of parameters without any significant F1 loss. |
|
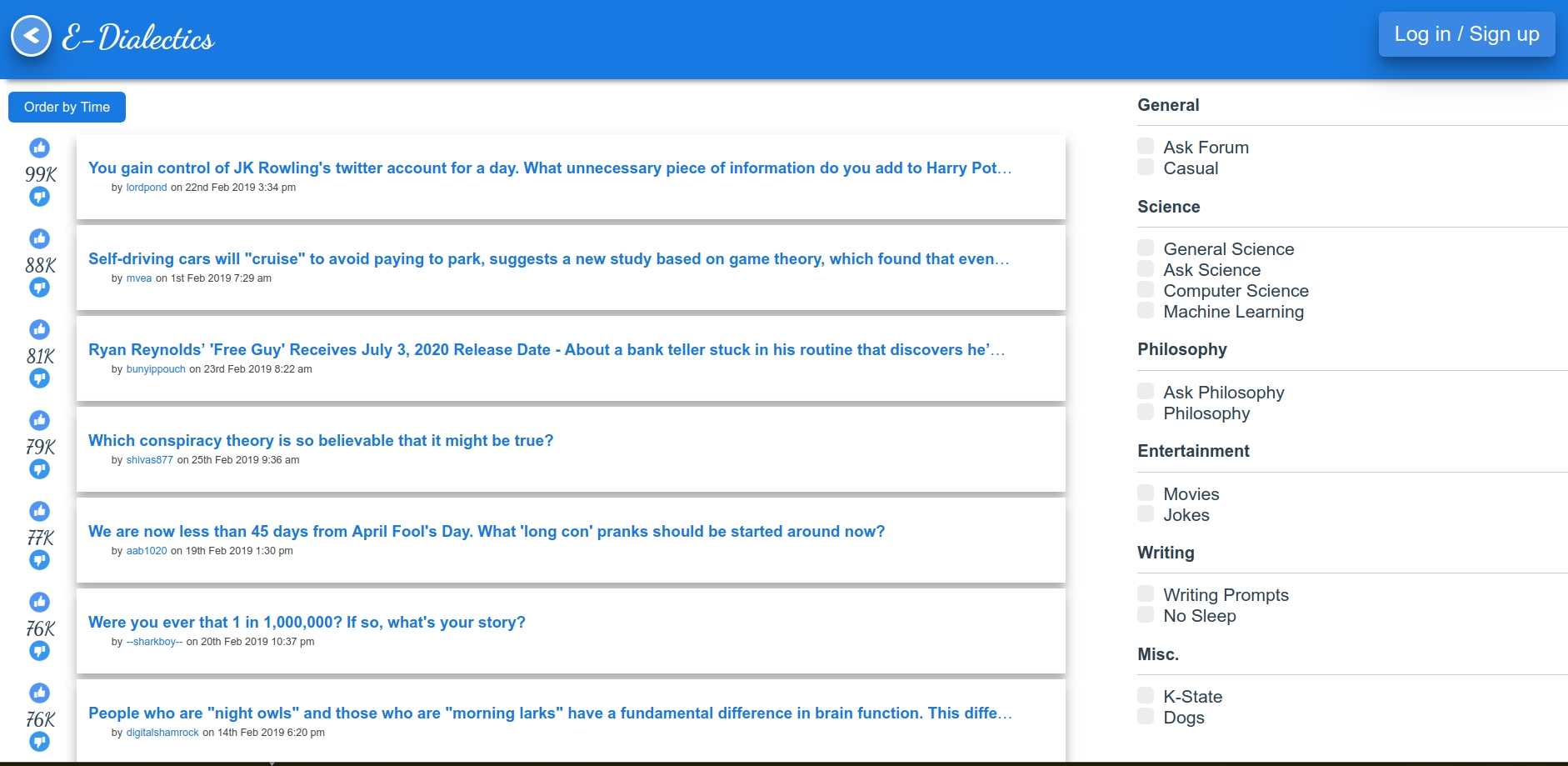
code The project is inspired by Reddit and the initial data is populated from a sample of real Reddit data that was retrieved using Google Big Query. The database is implemented using both SQL and NoSQL technologies in a complementary fashion. Users of E-Dialectics can read discussion threads and the comments for them, which are created by other users; each thread can also be under different subforums (eg. philosophy, computer science, science etc.). Anyone can read the threads and comments, but to be able to interact further they must log in to the site; new users can create their own accounts. Users can then create new threads and comments after they log into their accounts. |
|
Unsupervised extractive summarization using RAKE (code). Unsupervised keyphrase extraction using RAKE (code). Unsupervised extractive summarization using TextRank (code). Unsupervised keyphrase extraction using TextRank (code). |

|
Abstractive Summarization with RNNs (code). Machine Translation using Transformers (code). Abstractive Summarization with intra-attention-based LSTM encoder (code). |

|
|

|
code Experiment with Wide-ResNet and ResNeXt on CIFAR10 for image classification. Final Year project for Bachelors. |
|
|
|
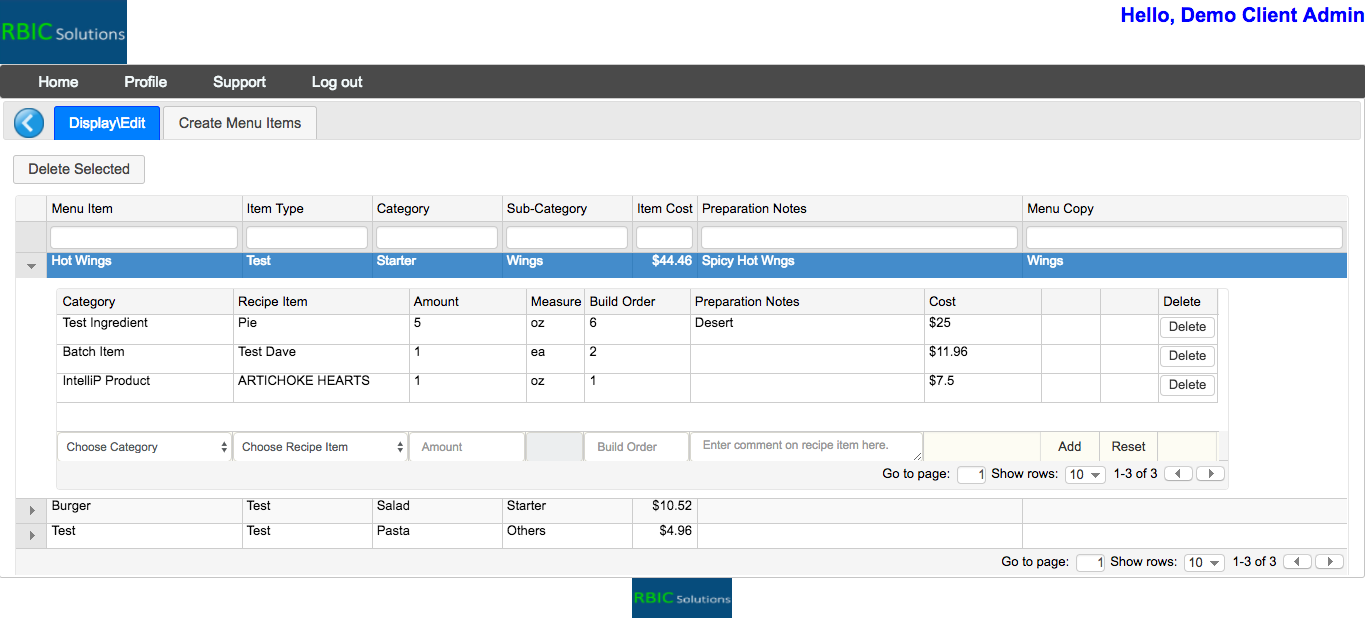
A full-stack software connected to a database that allows restaurants to manage menus, recipes, ingredients, and food costs, among other information. This was a freelance project. I engaged in full-stack development, including the design of databases, queries, frontend UI design, and some backend programming. |
|
|